When watching IPTV, you likely expect a smooth, clear picture without buffering or quality drops. However, stable streaming doesn’t depend solely on your internet speed or device quality. One of the key factors is the data transmission technology your provider uses. In this article, we’ll explore multicast transmission, how it works, and why it plays a crucial role in delivering efficient IPTV content delivery.
Multicast: The Foundation of Efficient and Stable Streaming
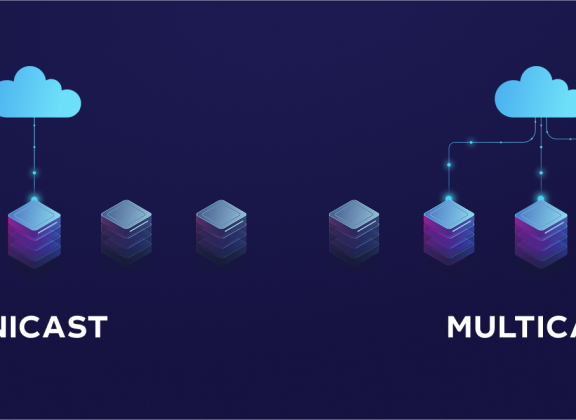
Multicast is a method of data transmission in IP networks that allows a single video stream to be delivered to multiple recipients at once, without duplicating it for each viewer. This stands in contrast to unicast, where every user receives an individual stream—even if they’re watching the exact same channel.
For example: if 100 users on the same network watch the same IPTV channel via multicast, the traffic is sent from the server just once and then replicated at the router level. With unicast, the server must send 100 separate streams—putting 100 times more load on the network. This highlights the bandwidth difference between multicast vs unicast IPTV.
Why Multicast Is Important for IPTV
The method used to deliver IPTV streams affects various aspects of performance.
IPTV bandwidth optimization. Multicast dramatically reduces the load on a network. With unicast, each viewer adds a new data stream, meaning more traffic on the server and internet link. Multicast solves this: the traffic remains stable regardless of the number of users—especially in local area networks.
Improved stability and quality. Because multicast doesn’t overload the server, it helps maintain a consistent bitrate and minimizes transmission errors. This is vital for IPTV streaming without buffering, especially during live content like sports, news, or events where even a second’s delay can ruin the experience. Reducing IPTV latency with multicast leads to a much smoother stream.
Faster channel switching. Multicast streams are already active in the network. So when you switch channels, your IPTV device simply “joins” a multicast group in IPTV networks. This enables near-instant switching without waiting for buffering.
What’s Needed for Multicast to Work
To use multicast effectively, several conditions must be met:
Provider-side support. Not all IPTV providers use multicast—some rely solely on unicast delivery. Compatible IPTV app or set-top box. The app or device must support joining multicast groups and handling multicast routing.
Proper router configuration. Your home router needs to support the IGMP protocol (Internet Group Management Protocol), which is how devices subscribe to multicast streams.
Wired connection. Multicast works best over Ethernet. Wireless connections may suffer from network packet loss and latency issues.
These elements are essential to leverage the benefits of multicast for IPTV streaming.
What If Multicast Isn’t Available?
Some providers deliver IPTV only over unicast, particularly when streaming over the internet rather than within a managed local network. In such cases:
- Ensure your device or player supports buffering
- Check your internet speed—especially during peak hours
- Use IPTV apps that support auto-reconnection features
- Consider using a VPN if routing issues are causing drops or instability
Even without multicast, you can improve your IPTV QoS (quality of service) by optimizing your network setup and player settings.
Multicast isn’t just a technical buzzword—it’s a core infrastructure feature that enables stable, efficient IPTV content delivery. If your IPTV provider and home network support multicast, you’ll benefit from faster switching, higher quality, and less buffering—even with multiple users. Always check whether a service and your equipment support multicast configuration for IPTV, and how you can enable it within your network. Taking that small step can significantly enhance your home viewing experience.